How to set up port forwarding for a broadband router or a firewall manually?
1. First you have to find out the IP address of your FTP server, as shown in Figure 1 below. If you don't know what is your network's structure (whether it is behind a router or a firewall), you can figure it out by the IP address of the FTP server.
If the IP address is the private IP within 192.168.*.* or 10.*.*.* or 172.13.* .*- 172.32.*.*, then the server could be located behind a NAT device (ADSL/Cable router is the common NAT device). Users from the public internet could not access your FTP server directly by using this private IP. Since your server is located behind a NAT device, this NAT device must have a WAN interface with a public IP address, which is accessible by users from the public internet. You have to set up the FTP server to use the WAN interface IP or domain name of this WAN interface.
However, if your FTP server's IP is not within the above private IP ranges, your server must use public IP. Your FTP server could only be behind a firewall. In that case, you may only need to open a range of PASV ports for the FTP server.
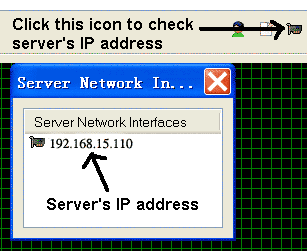
Figure 1. How to find your FTP server's IP address?
2. You need to find out your ADSL/Cable router's WAN interface IP. If your ISP won't give you a fixed IP address to the WAN interface of your router (Every time your router reboots, the WAN interface IP will change), you will need to apply a DDNS name (dynamic domain name service) for this WAN interface. Users will then always access your FTP server by using this domain name. You could apply a free DDNS name from DDNS service providers such as dyndns.org, NO-IP.com etc. In this example, we use the account "testuser" of DynDNS.org and the DDNS name "myftp.blogdns.org" for the WAN interface. Many routers had embedded some popular DDNS service providers. To show how to set up a DynDNS.org account for DDNS support, we will use the Linksys router in Figure 2 as an example.
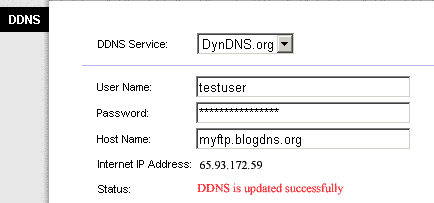
Figure 2. Setup DDNS support for the DynDNS.org account in the Linksys router
3. You have to choose a range of ports used for passive mode FTP. (If you don't know what is passive mode FTP, you can find the answer from Google.) You should better choose a port range above 10000 since this will reduce the chance of ports conflicting with other applications. In this example, we choose port range 60010 - 60030.
4. You have to set up the above DDNS and passive port ranges for your FTP server. Go to "Global Options->General->NAT and Firewall" as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. NAT and firewall settings
Click the "Setup..." button in Figure 3. Set the passive port range and the domain name of WAN interface as shown in the figure 4.
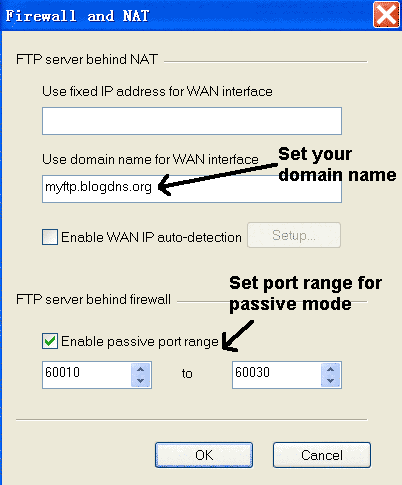
Figure 4. Passive port range and WAN interface domain name
5. Now you have to set up port forwarding in the router. The purpose of port forwarding is to open up ports in the router so that outside traffic to the opened ports will be forwarded directly to the internal FTP server.
Before setting up port forwarding inside the router, you must make sure the machine of your FTP server is using fixed IP instead of dynamic IP from DHCP.
This is very important because port forwarding requires destination IP to be fixed. If your server is using dynamic IP from DHCP, the next time the IP changes, port forwarding settings will become invalid.
In our example, the machine of the FTP server is using the fixed private IP 192.168.15.110.
Then you have to set up port forwarding for both standard FTP control port 21 and passive mode port range 60010-60030. We use the Linksys router as shown in Figure 5. Different routers may have different menus for port forwarding, so you may need to read the router manual. Note, that some special types of firewalls may require opening outgoing port 20, please check the troubleshooting section below for detailed information.
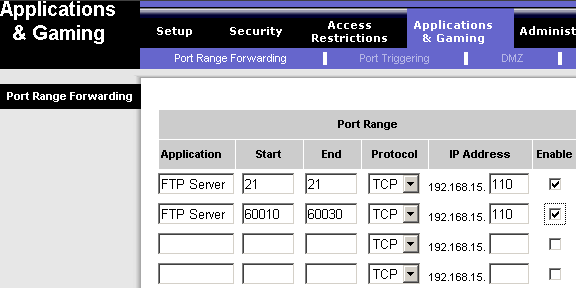
Figure 5. Setup port forwarding for FTP server inside Linksys router
1. If a user can not connect to the FTP server from outside (public internet). Click the log icon from Xlight's main program window, and check your server's logs on the screen. If you can not see any connections from outside, you might not configure your router or firewall correctly. Possible reasons are port forwarding for standard FTP control port 21 is not set up correctly inside your router/firewall or your FTP server's IP is different from the destination IP of port forwarding settings.
If you can see FTP connection logs from outside, but users from outside failed to get the directory list, then there is something wrong with the port forwarding setting for passive mode port ranges. Inside the FTP logs, find the FTP server's response after the client sends the PASV command. The server response will look like this:
227 Entering Passive Mode (65,93,172,59,m,n)
Inside the above response, m,n is used by the FTP client to calculate the PASV port it will connect to, the algorithm is m*256+n. For example, if m=10, n=20, then the PASV port opened by the server is 10*256+20=2580.
Check whether this port is within the PASV port ranges in the FTP server. Also, you need to check whether your FTP server's IP is different from the destination IP inside port forwarding settings
2. Make sure your WAN IP has been used by the FTP server in its response. The IP (x,x,x,x) inside server response "227 Entering Passive Mode (x,x,x,x,m,n) m, n" should be the IP address of your WAN interface.
3. Some firewalls, especially software-based firewalls will block outgoing traffic. So this kind of firewall may block port 20 for outgoing traffic, which port 20 is used for FTP PORT command. If the PORT command can't work, you may happen to have this kind of firewall and need to open port 20 for outgoing traffic in your firewall